MySQL Sample Databases
MySQL Sample Databases
MySQL Sample Databases
There are many excellent and interesting sample databases available, that you can use as a template (or pattern) to design your own databases.
1. MySQL's Sample Employee Database
Reference: MySQL's Sample Employees Database @ http://dev.mysql.com/doc/employee/en/index.html.
This is a rather simple database with 6 tables but with millions of records.
1.1 Database and Tables
There are 6 tables as follows:
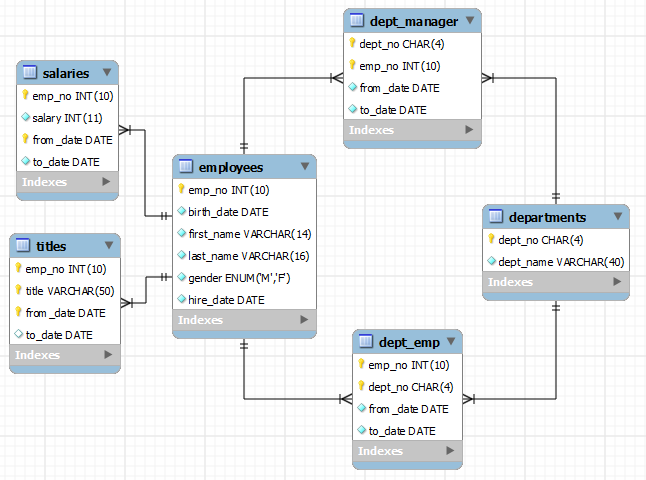
Table "employees"
CREATE TABLE employees (
emp_no INT NOT NULL, -- UNSIGNED AUTO_INCREMENT??
birth_date DATE NOT NULL,
first_name VARCHAR(14) NOT NULL,
last_name VARCHAR(16) NOT NULL,
gender ENUM ('M','F') NOT NULL, -- Enumeration of either 'M' or 'F'
hire_date DATE NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no) -- Index built automatically on primary-key column
-- INDEX (first_name)
-- INDEX (last_name)
);
There are 300,024 records for this table.
Table "departments"
CREATE TABLE departments (
dept_no CHAR(4) NOT NULL, -- in the form of 'dxxx'
dept_name VARCHAR(40) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (dept_no), -- Index built automatically
UNIQUE KEY (dept_name) -- Build INDEX on this unique-value column
);
The keyword KEY is synonym to INDEX. An INDEX can be built on unique-value column (UNIQUE KEY or UNIQUE INDEX) or non-unique-value column (KEY or INDEX). Indexes greatly facilitates fast search. However, they deplete the performance in INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE. Generally, relational databases are optimized for retrievals, and NOT for modifications.
There are 9 records for this table.
Table "dept_emp"
Junction table to support between many-to-many relationship between employees and departments. A department has many employees. An employee can belong to different department at different dates, and possibly concurrently.
CREATE TABLE dept_emp (
emp_no INT NOT NULL,
dept_no CHAR(4) NOT NULL,
from_date DATE NOT NULL,
to_date DATE NOT NULL,
KEY (emp_no), -- Build INDEX on this non-unique-value column
KEY (dept_no), -- Build INDEX on this non-unique-value column
FOREIGN KEY (emp_no) REFERENCES employees (emp_no) ON DELETE CASCADE,
-- Cascade DELETE from parent table 'employee' to this child table
-- If an emp_no is deleted from parent 'employee', all records
-- involving this emp_no in this child table are also deleted
-- ON UPDATE CASCADE??
FOREIGN KEY (dept_no) REFERENCES departments (dept_no) ON DELETE CASCADE,
-- ON UPDATE CASCADE??
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no, dept_no)
-- Might not be unique?? Need to include from_date
);
The foreign keys have ON DELETE reference action of CASCADE. If a record having a particular key-value from the parent table (employees and departments) is deleted, all the records in this child table having the same key-value are also deleted. Take note that the default ON DELETE reference action of is RESTRICTED, which disallows DELETE on the parent record, if there are matching records in the child table.
There are two reference actions: ON DELETE and ON UPDATE. The ON UPDATE reference action of is defaulted to RESTRICT (or disallow). It is more meaningful to set ON UPDATE to CASCADE, so that changes in parent table (e.g., change in emp_no and dept_no) can be cascaded down to the child table(s).
There are 331,603 records for this table.
Table "dept_manager"
join table to support between many-to-many relationship between employees and departments. Same structure as dept_emp.
CREATE TABLE dept_manager (
dept_no CHAR(4) NOT NULL,
emp_no INT NOT NULL,
from_date DATE NOT NULL,
to_date DATE NOT NULL,
KEY (emp_no),
KEY (dept_no),
FOREIGN KEY (emp_no) REFERENCES employees (emp_no) ON DELETE CASCADE,
-- ON UPDATE CASCADE??
FOREIGN KEY (dept_no) REFERENCES departments (dept_no) ON DELETE CASCADE,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no, dept_no) -- might not be unique?? Need from_date
);
There are 24 records for this table.
Table "titles"
There is a one-to-many relationship between employees and titles. One employee has many titles (concurrently or at different dates). A titles record refers to one employee (via emp_no).
CREATE TABLE titles (
emp_no INT NOT NULL,
title VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
from_date DATE NOT NULL,
to_date DATE,
KEY (emp_no),
FOREIGN KEY (emp_no) REFERENCES employees (emp_no) ON DELETE CASCADE,
-- ON UPDATE CASCADE??
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no, title, from_date)
-- This ensures unique combination.
-- An employee may hold the same title but at different period
);
There are 443,308 records for this table.
Table "salaries"
Similar structure to titles table. One-to-many relationship between employees and salaries.
CREATE TABLE salaries (
emp_no INT NOT NULL,
salary INT NOT NULL,
from_date DATE NOT NULL,
to_date DATE NOT NULL,
KEY (emp_no),
FOREIGN KEY (emp_no) REFERENCES employees (emp_no) ON DELETE CASCADE,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no, from_date)
);
There are 2,844,047 records for this table.
1.2 Stored Objects
No stored objects (view, procedure, function, trigger, event) defined. [Shall try!]
2. MySQL's Sample Salika (DVD Rental) Database
Reference: MySQL's Sample Sakila Database @ http://dev.mysql.com/doc/sakila/en/index.html.
The MySQL's Sample Salika (DVD Rental) Database can be downloaded fromhttp://dev.mysql.com/doc/sakila/en/index.html. It is a complex database with 16 tables. It also illustrates features such as Views, Stored Procedures and Triggers. This is probably the best sample available for studying MySQL databases.
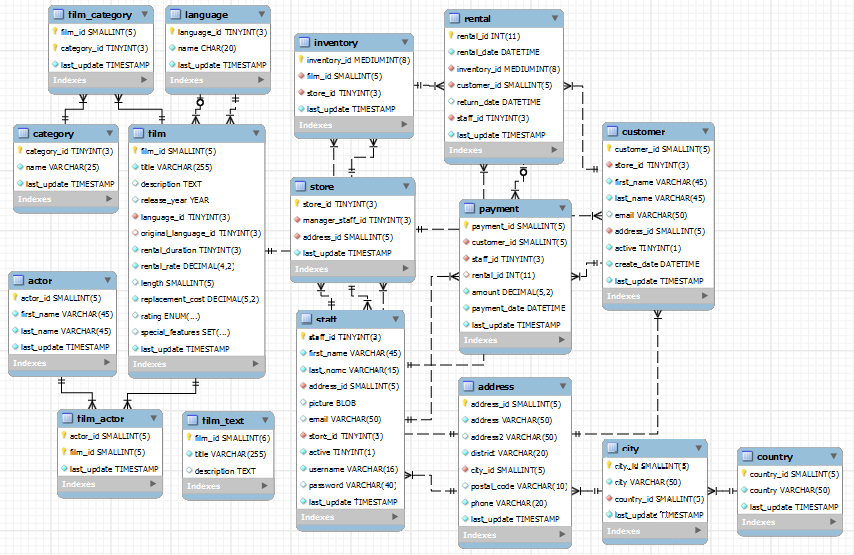
2.1 Database and Tables
All the tables have DEFAULT CHARSET of utf8 for internationalization support. All the tables, except film_text, use InnoDB engine, which supports foreign key and transaction. The table film_text uses MyISAM to support FULLTEXT search.
For UTF8 support, we could set the DEFAULT CHARSET at the database level as follows:
-- Enable client program to communicate with the server using utf8 character set
SET NAMES 'utf8';
DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS `sakila`;
-- Set the default charset to utf8 for internationalization, use case-insensitive (ci) collation
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS `sakila` DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci;
USE `sakila`;
We could use "SHOW CREATE DATABASE databaseName \G" and "SHOW CREATE TABLE tableName \G" to display all the defaults used in CREATE DATABASE and CREATE TABLE.
Table "actor"
CREATE TABLE actor (
actor_id SMALLINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
-- 16-bit unsigned int in the range of [0, 65535]
first_name VARCHAR(45) NOT NULL,
last_name VARCHAR(45) NOT NULL,
last_update TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY (actor_id),
KEY idx_actor_last_name (last_name) -- To build index (non-unique) on last_name
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
-- Use InnoDB Engine, which supports foreign key and transaction
-- Use Unicode 'utf8' character set for this table
- There can be one
TIMESTAMPcolumn withDEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP. If you wish to have bothcreateandlast_update, you need to use aON INSERTtrigger to set thecreateTIMESTAMP. For strict auditing, you might havecreate_timestamp,create_by,last_update_timestampandlast_update_by. - InnoDB engine is used, which support foreign key and transaction.
- The default character set for this table is UTF8, which supports all languages for internationalization.
- Better to use
INT UNSIGNEDforAUTO_INCREMENTcolumnactor_idto avoid overrun.
There are 200 records for this table.
Table "language"
Languages: such as English, Italian, Japanese, Mandrain, Cantonese, French, German.
CREATE TABLE language (
language_id TINYINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
-- 8-bit unsigned int [0, 255]
name CHAR(20) NOT NULL,
last_update TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY (language_id)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
May be simpler to use an ENUM (one choice).
There are 6 records for this table, i.e., 'English', 'Italian', 'Japanese', 'Mandarin', 'French', 'German'.
Table "film"
CREATE TABLE film (
film_id SMALLINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
title VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
description TEXT DEFAULT NULL, -- Up to 64KB
release_year YEAR DEFAULT NULL, -- 'yyyy'
language_id TINYINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, -- 8-bit unsigned int [0, 255]
original_language_id TINYINT UNSIGNED DEFAULT NULL,
rental_duration TINYINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL DEFAULT 3,
rental_rate DECIMAL(4,2) NOT NULL DEFAULT 4.99,
-- DECIMAL is precise and ideal for currency [99.99]. UNSIGNED?
length SMALLINT UNSIGNED DEFAULT NULL, -- 16-bit unsigned int [0, 65535]
replacement_cost DECIMAL(5,2) NOT NULL DEFAULT 19.99, -- [999.99], UNSIGNED??
rating ENUM('G','PG','PG-13','R','NC-17') DEFAULT 'G',
special_features SET('Trailers','Commentaries','Deleted Scenes','Behind the Scenes') DEFAULT NULL,
-- Can take zero or more values from a SET
-- But only one value from ENUM
last_update TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY (film_id),
KEY idx_title (title),
KEY idx_fk_language_id (language_id),
KEY idx_fk_original_language_id (original_language_id),
-- To build index on title, language_id, original_language_id and film_id (primary key)
CONSTRAINT fk_film_language FOREIGN KEY (language_id) REFERENCES language (language_id)
ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE CASCADE,
-- Cannot delete parent record if there is any matching child record
-- Update the matching child records if parent record is updated
CONSTRAINT fk_film_language_original FOREIGN KEY (original_language_id) REFERENCES language (language_id)
ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE CASCADE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
- Instead of hard-coding the "language" and "original language", it uses
language_idto look up thelanguagetable, in a one-to-one relationship. Could use anENUMfor language directly for simplicity. KEYs(INDEXes) are defined on certain columns to facilitate fast search on these columns. We would use "SHOW INDEX FROM tableName \G" to display the details on indexes.- Should include
UNSIGNEDfor for non-negative numeric columns likerental_rate.
There are 1000 records for this table.
Table "film_actor"
Junction table between actor and film to support the many-to-many relationship.
CREATE TABLE film_actor (
actor_id SMALLINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
film_id SMALLINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
last_update TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY (actor_id, film_id),
KEY idx_fk_film_id (`film_id`),
CONSTRAINT fk_film_actor_actor FOREIGN KEY (actor_id) REFERENCES actor (actor_id)
ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE CASCADE,
CONSTRAINT fk_film_actor_film FOREIGN KEY (film_id) REFERENCES film (film_id)
ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE CASCADE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
There are 5462 records for this table.
Table "category"
CREATE TABLE category (
category_id TINYINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
name VARCHAR(25) NOT NULL,
last_update TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY (category_id)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
- There are 16 records for this table, i.e.,
'Action','Animation','Children','Classics','Comedy','Documentary','Drama','Family','Foreign','Games','Horror','Music','New','Sci-Fi','Sports','Travel'. - May be better to use a
SETto support multiple categories per film, if the number of categories is small. ASETis limited to 64 items in MySQL.
Table "film_category"
Junction table to support many-to-many relationship between film and category.
CREATE TABLE film_category (
film_id SMALLINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
category_id TINYINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
last_update TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY (film_id, category_id),
CONSTRAINT fk_film_category_film FOREIGN KEY (film_id) REFERENCES film (film_id)
ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE CASCADE,
CONSTRAINT fk_film_category_category FOREIGN KEY (category_id) REFERENCES category (category_id)
ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE CASCADE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
There are 1000 records for this table. Each of the 1000 films has ONE category.
Table "film_text" - FULLTEXT Index and Search
CREATE TABLE film_text (
film_id SMALLINT NOT NULL,
title VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
description TEXT,
PRIMARY KEY (film_id),
FULLTEXT KEY idx_title_description (title, description)
-- To build index on FULLTEXT to facilitate text search
-- FULLTEXT is supported in MyISAM engine, NOT in InnoDB engine
) ENGINE=MyISAM DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
- This table duplicates information from
filmtable, to supportFULLTEXTsearch. That is, user can efficiently search all the words intitleanddescriptioncolumns. - To ensure consistency between
film_textandfilm, the rows are inserted/updated via a trigger onfilmtable. FULLTEXTsearch is supported inMyISAMengine only, not theInnoDBengine. AFULLTEXTindex is build on columns(title, description). You can performFULLTEXTsearch on the index using "WHERE MATCH(columns) AGAINST(words)", for example,mysql> SELECT * FROM film_text WHERE MATCH(title, description) AGAINST ('great'); -- search for the given word on the FULLTEXT index columns mysql> SELECT * FROM film_text WHERE MATCH(title, description) AGAINST ('great good'); -- search for either 'great' or 'good' mysql> SELECT * FROM film_text WHERE MATCH(title, description) AGAINST ('"very good"' IN BOOLEAN MODE); -- Use BOOLEAN MODE to match exact phrase (enclosed in double-quotes) mysql> SELECT * FROM film_text WHERE MATCH(title, description) AGAINST ('+good -bad' IN BOOLEAN MODE); -- Use BOOLEAN MODE to search for the word 'good', but NOT the word 'bad' mysql> SELECT * FROM film_text WHERE MATCH(title, description) AGAINST ('great*' IN BOOLEAN MODE); -- In BOOLEAN MODE, wildcard * matches zero or more characters mysql> SELECT * FROM film_text WHERE MATCH(title, description) AGAINST ('great' WITH QUERY EXPANSION); -- Do a second search on words in the most relevant rows from the first search
There are 1000 records for this table. Each film record has a film_text counterpart. The records in the film_text table is created via a INSERT trigger on the film table.
Table "inventory"
The company could have many copies of a particular film (in one store or many stores). Each copy is represented by an inventory record. The store is linked thru store_id to the table store.
CREATE TABLE inventory (
inventory_id MEDIUMINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
-- Simpler to use INT UNSIGNED
film_id SMALLINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
store_id TINYINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
last_update TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY (inventory_id),
KEY idx_fk_film_id (film_id),
KEY idx_store_id_film_id (store_id, film_id),
CONSTRAINT fk_inventory_store FOREIGN KEY (store_id) REFERENCES store (store_id)
ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE CASCADE,
CONSTRAINT fk_inventory_film FOREIGN KEY (film_id) REFERENCES film (film_id)
ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE CASCADE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
There are 4581 records for this table.
Table "store"
Each store has a manager, linked thru manager_staff_id to the staff table. The address of the store is also linked thru address_id to the address table.
CREATE TABLE store (
store_id TINYINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
manager_staff_id TINYINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
address_id SMALLINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
last_update TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY (store_id),
UNIQUE KEY idx_unique_manager (manager_staff_id), -- one manager manages only one store
KEY idx_fk_address_id (address_id),
CONSTRAINT fk_store_staff FOREIGN KEY (manager_staff_id) REFERENCES staff (staff_id)
ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE CASCADE,
CONSTRAINT fk_store_address FOREIGN KEY (address_id) REFERENCES address (address_id)
ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE CASCADE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
There are 2 records for this table.
Table "staff"
CREATE TABLE staff (
staff_id TINYINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
first_name VARCHAR(45) NOT NULL,
last_name VARCHAR(45) NOT NULL,
address_id SMALLINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
picture BLOB DEFAULT NULL, -- Kept a picture as BLOB (up to 64KB)
email VARCHAR(50) DEFAULT NULL,
store_id TINYINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
active BOOLEAN NOT NULL DEFAULT TRUE, -- BOOLEAN FALSE (0) TRUE (non-0)
username VARCHAR(16) NOT NULL,
password VARCHAR(40) BINARY DEFAULT NULL, -- BINARY??
last_update TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY (staff_id),
KEY idx_fk_store_id (store_id),
KEY idx_fk_address_id (address_id),
CONSTRAINT fk_staff_store FOREIGN KEY (store_id) REFERENCES store (store_id)
ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE CASCADE,
CONSTRAINT fk_staff_address FOREIGN KEY (address_id) REFERENCES address (address_id)
ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE CASCADE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
There are 2 records for this table, with pictures (BLOB) provided.
Table "customer"
CREATE TABLE customer (
customer_id SMALLINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
store_id TINYINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
first_name VARCHAR(45) NOT NULL,
last_name VARCHAR(45) NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR(50) DEFAULT NULL,
address_id SMALLINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
active BOOLEAN NOT NULL DEFAULT TRUE,
create_date DATETIME NOT NULL,
last_update TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY (customer_id),
KEY idx_fk_store_id (store_id),
KEY idx_fk_address_id (address_id),
KEY idx_last_name (last_name),
CONSTRAINT fk_customer_address FOREIGN KEY (address_id) REFERENCES address (address_id)
ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE CASCADE,
CONSTRAINT fk_customer_store FOREIGN KEY (store_id) REFERENCES store (store_id)
ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE CASCADE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
There are 599 records for this table.
Table "rental"
Rental rate is kept in the film table.
CREATE TABLE rental (
rental_id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
rental_date DATETIME NOT NULL,
inventory_id MEDIUMINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
customer_id SMALLINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
return_date DATETIME DEFAULT NULL,
staff_id TINYINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
last_update TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY (rental_id),
UNIQUE KEY (rental_date, inventory_id, customer_id),
KEY idx_fk_inventory_id (inventory_id),
KEY idx_fk_customer_id (customer_id),
KEY idx_fk_staff_id (staff_id),
CONSTRAINT fk_rental_staff FOREIGN KEY (staff_id) REFERENCES staff (staff_id)
ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE CASCADE,
CONSTRAINT fk_rental_inventory FOREIGN KEY (inventory_id) REFERENCES inventory (inventory_id)
ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE CASCADE,
CONSTRAINT fk_rental_customer FOREIGN KEY (customer_id) REFERENCES customer (customer_id)
ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE CASCADE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
There are 16,044 records for this table.
Table "payment"
An rental can have multiple payments?
CREATE TABLE payment (
payment_id SMALLINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
customer_id SMALLINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
staff_id TINYINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
rental_id INT DEFAULT NULL,
amount DECIMAL(5,2) NOT NULL,
payment_date DATETIME NOT NULL,
last_update TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY (payment_id),
KEY idx_fk_staff_id (staff_id),
KEY idx_fk_customer_id (customer_id),
CONSTRAINT fk_payment_rental FOREIGN KEY (rental_id) REFERENCES rental (rental_id)
ON DELETE SET NULL ON UPDATE CASCADE,
CONSTRAINT fk_payment_customer FOREIGN KEY (customer_id) REFERENCES customer (customer_id)
ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE CASCADE,
CONSTRAINT fk_payment_staff FOREIGN KEY (staff_id) REFERENCES staff (staff_id)
ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE CASCADE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
There are 16,049 records for this table, more than rental table.
Table "address"
It is unlikely that two persons share the same address. Address is often a required field for a rental transaction. So it is probably better to store directly inside the customers table.
CREATE TABLE address (
address_id SMALLINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
address VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
address2 VARCHAR(50) DEFAULT NULL,
district VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
city_id SMALLINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
postal_code VARCHAR(10) DEFAULT NULL,
phone VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
last_update TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY (address_id),
KEY idx_fk_city_id (city_id),
CONSTRAINT `fk_address_city` FOREIGN KEY (city_id) REFERENCES city (city_id)
ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE CASCADE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
There are 603 records for this table.
Table "city"
CREATE TABLE city (
city_id SMALLINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
city VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
country_id SMALLINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
last_update TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY (city_id),
KEY idx_fk_country_id (country_id),
CONSTRAINT `fk_city_country` FOREIGN KEY (country_id) REFERENCES country (country_id)
ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE CASCADE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
There are 600 records for this table.
Table "country"
Having a country table may facilitate the creation of pull-down menu. Alternatively, you could consider using an ENUM (number of countries may exceed ENUM's limit). For city, there are just too many cities in the world that the list can never be exhaustive. Probably better to keep inside the address table.
CREATE TABLE country (
country_id SMALLINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
country VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
last_update TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY (country_id)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
There are 109 records for this table.
2.2 Views
A VIEW is a virtual table (without data) that provides an alternate way to look at the data. It could be a consolidated set of columns from multiple table, or include derived column (such as total price).
We could use "SHOW CREATE VIEW viewName \G" to show all the defaults.
View "staff_list"
CREATE VIEW staff_list
AS
SELECT
s.staff_id AS ID,
CONCAT(s.first_name, _utf8' ', s.last_name) AS name,
a.address AS address,
a.postal_code AS `zip code`,
a.phone AS phone,
city.city AS city,
country.country AS country,
s.store_id AS SID
FROM staff AS s
JOIN address AS a ON s.address_id = a.address_id
JOIN city ON a.city_id = city.city_id
JOIN country ON city.country_id = country.country_id;
- String literal can be expressed with optional introducer and collation in the form of:
-- Syntax [_charsetName]'stringLiteral' [COLLATE collationName] -- Example SELECT _utf8' '; -- space in UTF8
For Example,
mysql> SELECT * FROM staff_list;
+----+--------------+----------------------+----------+-------------+------------+-----------+-----+
| ID | name | address | zip code | phone | city | country | SID |
+----+--------------+----------------------+----------+-------------+------------+-----------+-----+
| 1 | Mike Hillyer | 23 Workhaven Lane | | 14033335568 | Lethbridge | Canada | 1 |
| 2 | Jon Stephens | 1411 Lillydale Drive | | 6172235589 | Woodridge | Australia | 2 |
+----+--------------+----------------------+----------+-------------+------------+-----------+-----+
View "customer_list"
CREATE VIEW customer_list
AS
SELECT
cu.customer_id AS ID,
CONCAT(cu.first_name, _utf8' ', cu.last_name) AS name,
a.address AS address,
a.postal_code AS `zip code`,
a.phone AS phone,
city.city AS city,
country.country AS country,
IF(cu.active, _utf8'active', _utf8'') AS notes,
cu.store_id AS SID
FROM customer AS cu
JOIN address AS a ON cu.address_id = a.address_id
JOIN city ON a.city_id = city.city_id
JOIN country ON city.country_id = country.country_id;
View "film_list"
CREATE VIEW film_list
AS
SELECT
film.film_id AS FID,
film.title AS title,
film.description AS description,
category.name AS category,
film.rental_rate AS price,
film.length AS length,
film.rating AS rating,
GROUP_CONCAT(CONCAT(actor.first_name, _utf8' ', actor.last_name) SEPARATOR ', ') AS actors
FROM category
LEFT JOIN film_category ON category.category_id = film_category.category_id
LEFT JOIN film ON film_category.film_id = film.film_id
JOIN film_actor ON film.film_id = film_actor.film_id
JOIN actor ON film_actor.actor_id = actor.actor_id
GROUP BY film.film_id;
- The
GROUP_CONCAT(col SEPARATOR str)GROUP BYaggregate function can be used to produce a concatenate string for each group returned by theGROUP BYclause. Eachfilm_id(inGROUP BY) has many actors. - For example,
mysql> SELECT * FROM film_list LIMIT 1 \G *************************** 1. row *************************** FID: 1 title: ACADEMY DINOSAUR description: A Epic Drama of a Feminist And a Mad Scientist who must Battle a Teacher in The Canadian Rockies category: Documentary price: 0.99 length: 86 rating: PG actors: PENELOPE GUINESS, CHRISTIAN GABLE, LUCILLE TRACY, SANDRA PECK, JOHNNY CAGE, MENA TEMPLE, WARREN NOLTE, OPRAH KILMER, ROCK DUKAKIS, MARY KEITEL
View "nicer_but_slower_film_list"
CREATE VIEW nicer_but_slower_film_list
AS
SELECT
film.film_id AS FID,
film.title AS title,
film.description AS description,
category.name AS category,
film.rental_rate AS price,
film.length AS length,
film.rating AS rating,
GROUP_CONCAT(
CONCAT(
CONCAT(UCASE(SUBSTR(actor.first_name, 1, 1)), -- first_name initial-cap
LCASE(SUBSTR(actor.first_name, 2, LENGTH(actor.first_name))),
_utf8' ', -- space
CONCAT(UCASE(SUBSTR(actor.last_name, 1, 1)), -- last_name initial-cap
LCASE(SUBSTR(actor.last_name, 2, LENGTH(actor.last_name)))))) -- end of outer CONCAT
SEPARATOR ', ') AS actors
FROM category
LEFT JOIN film_category ON category.category_id = film_category.category_id
LEFT JOIN film ON film_category.film_id = film.film_id
JOIN film_actor ON film.film_id = film_actor.film_id
JOIN actor ON film_actor.actor_id = actor.actor_id
GROUP BY film.film_id;
- The complex
CONCAT()is used to produce camel-case (initial-capitalized) for thefirst_nameandlast_name, e.g., "Penelope Guiness". LENGTH(str)returns the length of the string.SUBSTR(str, fromIndex, length)returns the substring from index of length (index begins at 1).UCASE(str)andLCASE(str)returns the uppercase and lowercase.- This view is exactly the same as
film_listview. Why is it callednicer_but_slower_film_list?
View "sales_by_store"
CREATE VIEW sales_by_store
AS
SELECT
CONCAT(c.city, _utf8',', cy.country) AS store,
CONCAT(m.first_name, _utf8' ', m.last_name) AS manager,
SUM(p.amount) AS total_sales
FROM payment AS p
INNER JOIN rental AS r ON p.rental_id = r.rental_id
INNER JOIN inventory AS i ON r.inventory_id = i.inventory_id
INNER JOIN store AS s ON i.store_id = s.store_id
INNER JOIN address AS a ON s.address_id = a.address_id
INNER JOIN city AS c ON a.city_id = c.city_id
INNER JOIN country AS cy ON c.country_id = cy.country_id
INNER JOIN staff AS m ON s.manager_staff_id = m.staff_id
GROUP BY s.store_id
ORDER BY cy.country, c.city;
The SUM() GROUP BY aggregate function applies to each group of store_id, i.e., per store.
For example,
+---------------------+--------------+-------------+
| store | manager | total_sales |
+---------------------+--------------+-------------+
| Woodridge,Australia | Jon Stephens | 33726.77 |
| Lethbridge,Canada | Mike Hillyer | 33679.79 |
+---------------------+--------------+-------------+
View "sales_by_film_category"
CREATE VIEW sales_by_film_category
AS
SELECT
c.name AS category,
SUM(p.amount) AS total_sales
FROM payment AS p
INNER JOIN rental AS r ON p.rental_id = r.rental_id
INNER JOIN inventory AS i ON r.inventory_id = i.inventory_id
INNER JOIN film AS f ON i.film_id = f.film_id
INNER JOIN film_category AS fc ON f.film_id = fc.film_id
INNER JOIN category AS c ON fc.category_id = c.category_id
GROUP BY c.name
ORDER BY total_sales DESC;
The GROUP BY aggregate function SUM() applies to each group of c.name, i.e., per category's name.
View "actor_info"
CREATE
DEFINER=CURRENT_USER
SQL SECURITY INVOKER
VIEW actor_info
AS
SELECT
a.actor_id,
a.first_name,
a.last_name,
GROUP_CONCAT(
DISTINCT
CONCAT(c.name, ': ',
(SELECT
GROUP_CONCAT(f.title ORDER BY f.title SEPARATOR ', ')
FROM sakila.film f
INNER JOIN sakila.film_category fc ON f.film_id = fc.film_id
INNER JOIN sakila.film_actor fa ON f.film_id = fa.film_id
WHERE fc.category_id = c.category_id AND fa.actor_id = a.actor_id)
) -- end CONCAT
ORDER BY c.name
SEPARATOR '; ') AS film_info
FROM sakila.actor a
LEFT JOIN sakila.film_actor fa ON a.actor_id = fa.actor_id
LEFT JOIN sakila.film_category fc ON fa.film_id = fc.film_id
LEFT JOIN sakila.category c ON fc.category_id = c.category_id
GROUP BY
a.actor_id,
a.first_name,
a.last_name;
SQL SECURITY INVOKERspecifies that the it executes with the privileges of the user who invoke it (instead of theDEFINER).GROUP_CONCAT([DISTINCT] col [ORDER BY ...] [SEPARATOR ...]): You can apply optionalDISTINCTandORDER BYtoGROUP_CONCAT().- For example,
mysql> SELECT * FROM actor_info LIMIT 1 \G *************************** 1. row *************************** actor_id: 1 first_name: PENELOPE last_name: GUINESS film_info: Animation: ANACONDA CONFESSIONS; Children: LANGUAGE COWBOY; Classics: COLOR PHILADELPHIA, WESTWARD SEABISCUIT; ......
2.3 Stored Routines: Procedures and Functions
Procedure "rewards_report"
-- Change the MySQL statement delimiter to // as it crashes with procedure's delimiter ';'
DELIMITER //
CREATE PROCEDURE rewards_report (
IN min_monthly_purchases TINYINT UNSIGNED, -- min number of purchases
IN min_dollar_amount_purchased DECIMAL(10,2) UNSIGNED, -- min dollar amount purchased
OUT count_rewardees INT -- number of customers to be rewarded
)
LANGUAGE SQL
NOT DETERMINISTIC
READS SQL DATA
SQL SECURITY DEFINER
COMMENT 'Provides a customizable report on best customers'
proc: BEGIN
DECLARE last_month_start DATE;
DECLARE last_month_end DATE;
/* Some sanity checks... */
IF min_monthly_purchases = 0 THEN
SELECT 'Minimum monthly purchases parameter must be > 0';
LEAVE proc;
END IF;
IF min_dollar_amount_purchased = 0.00 THEN
SELECT 'Minimum monthly dollar amount purchased parameter must be > $0.00';
LEAVE proc;
END IF;
/* Determine start and end time periods */
SET last_month_start = DATE_SUB(CURRENT_DATE(), INTERVAL 1 MONTH);
SET last_month_start = STR_TO_DATE(
CONCAT(YEAR(last_month_start), '-', MONTH(last_month_start), '-01'),
'%Y-%m-%d');
SET last_month_end = LAST_DAY(last_month_start);
/* Create a temporary storage area for Customer IDs */
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE tmpCustomer (customer_id SMALLINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY);
/* Find all customers meeting the monthly purchase requirements */
INSERT INTO tmpCustomer (customer_id)
SELECT p.customer_id
FROM payment AS p
WHERE DATE(p.payment_date) BETWEEN last_month_start AND last_month_end
GROUP BY customer_id
HAVING
SUM(p.amount) > min_dollar_amount_purchased
AND COUNT(customer_id) > min_monthly_purchases;
/* Populate OUT parameter with count of found customers */
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM tmpCustomer INTO count_rewardees;
/* Output ALL customer information of matching rewardees.
Customize output as needed. */
SELECT c.*
FROM tmpCustomer AS t
INNER JOIN customer AS c ON t.customer_id = c.customer_id;
/* Clean up */
DROP TABLE tmpCustomer;
END //
-- Change the MySQL delimiter back to ';'
DELIMITER ;
To test the procedure,
mysql> CALL rewards_report(2, 10, @numRewardees);
mysel> SELECT @numRewardees;
Function "get_customer_balance"
DELIMITER $$
CREATE FUNCTION get_customer_balance(p_customer_id INT, p_effective_date DATETIME) RETURNS DECIMAL(5,2)
DETERMINISTIC
READS SQL DATA
BEGIN
# OK, WE NEED TO CALCULATE THE CURRENT BALANCE GIVEN A CUSTOMER_ID AND A DATE
# THAT WE WANT THE BALANCE TO BE EFFECTIVE FOR. THE BALANCE IS:
# 1) RENTAL FEES FOR ALL PREVIOUS RENTALS
# 2) ONE DOLLAR FOR EVERY DAY THE PREVIOUS RENTALS ARE OVERDUE
# 3) IF A FILM IS MORE THAN RENTAL_DURATION * 2 OVERDUE, CHARGE THE REPLACEMENT_COST
# 4) SUBTRACT ALL PAYMENTS MADE BEFORE THE DATE SPECIFIED
DECLARE v_rentfees DECIMAL(5,2); # FEES PAID TO RENT THE VIDEOS INITIALLY
DECLARE v_overfees INTEGER; # LATE FEES FOR PRIOR RENTALS
DECLARE v_payments DECIMAL(5,2); # SUM OF PAYMENTS MADE PREVIOUSLY
SELECT IFNULL(SUM(film.rental_rate), 0) INTO v_rentfees
FROM film, inventory, rental
WHERE film.film_id = inventory.film_id
AND inventory.inventory_id = rental.inventory_id
AND rental.rental_date <= p_effective_date
AND rental.customer_id = p_customer_id;
SELECT IFNULL(
SUM(
IF((TO_DAYS(rental.return_date) - TO_DAYS(rental.rental_date)) > film.rental_duration,
((TO_DAYS(rental.return_date) - TO_DAYS(rental.rental_date)) - film.rental_duration), 0)),
0)
INTO v_overfees
FROM rental, inventory, film
WHERE film.film_id = inventory.film_id
AND inventory.inventory_id = rental.inventory_id
AND rental.rental_date <= p_effective_date
AND rental.customer_id = p_customer_id;
SELECT IFNULL(SUM(payment.amount), 0) INTO v_payments
FROM payment
WHERE payment.payment_date <= p_effective_date
AND payment.customer_id = p_customer_id;
RETURN v_rentfees + v_overfees - v_payments;
END $$
DELIMITER ;
Procedure "film_in_stock"
DELIMITER $$
-- Given the film_id and store_id, find the film count
CREATE PROCEDURE film_in_stock(
IN p_film_id INT,
IN p_store_id INT,
OUT p_film_count INT)
READS SQL DATA
BEGIN
SELECT inventory_id
FROM inventory
WHERE film_id = p_film_id
AND store_id = p_store_id
AND inventory_in_stock(inventory_id);
SELECT FOUND_ROWS() INTO p_film_count;
END $$
DELIMITER ;
Procedure "film_not_in_stock"
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE film_not_in_stock(IN p_film_id INT, IN p_store_id INT, OUT p_film_count INT)
READS SQL DATA
BEGIN
SELECT inventory_id
FROM inventory
WHERE film_id = p_film_id
AND store_id = p_store_id
AND NOT inventory_in_stock(inventory_id);
SELECT FOUND_ROWS() INTO p_film_count;
END $$
DELIMITER ;
Function "inventory_held_by_customer"
DELIMITER $$
CREATE FUNCTION inventory_held_by_customer(p_inventory_id INT) RETURNS INT
READS SQL DATA
BEGIN
DECLARE v_customer_id INT;
DECLARE EXIT HANDLER FOR NOT FOUND RETURN NULL;
SELECT customer_id INTO v_customer_id
FROM rental
WHERE return_date IS NULL AND inventory_id = p_inventory_id;
RETURN v_customer_id;
END $$
DELIMITER ;
Function "inventory_in_stock"
DELIMITER $$
CREATE FUNCTION inventory_in_stock(p_inventory_id INT) RETURNS BOOLEAN
READS SQL DATA
BEGIN
DECLARE v_rentals INT;
DECLARE v_out INT;
# AN ITEM IS IN-STOCK IF THERE ARE EITHER NO ROWS IN THE rental TABLE
# FOR THE ITEM OR ALL ROWS HAVE return_date POPULATED
SELECT COUNT(*) INTO v_rentals
FROM rental
WHERE inventory_id = p_inventory_id;
IF v_rentals = 0 THEN
RETURN TRUE;
END IF;
SELECT COUNT(rental_id) INTO v_out
FROM inventory LEFT JOIN rental USING(inventory_id)
WHERE inventory.inventory_id = p_inventory_id AND rental.return_date IS NULL;
IF v_out > 0 THEN
RETURN FALSE;
ELSE
RETURN TRUE;
END IF;
END $$
DELIMITER ;
2.4 Triggers
The film_text table duplicates information from film table to build a FULLTEXT search index. To ensure consistency between the two tables, triggers are used for INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE on each row of film table, that perform corresponding actions in the film_text table.
Trigger "ins_film"
DELIMITER $$
-- Trigger for INSERT INTO film table
-- Copy information to film_text table
CREATE TRIGGER `ins_film` AFTER INSERT ON `film` FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
INSERT INTO film_text (film_id, title, description)
VALUES (new.film_id, new.title, new.description);
END$$
DELIMITER ;
Trigger "upd_film"
-- Trigger for UPDATE film table
-- Update the film_text table
DELIMITER $$
CREATE TRIGGER `upd_film` AFTER UPDATE ON `film` FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
IF (old.title != new.title) or (old.description != new.description)
THEN
UPDATE film_text
SET title=new.title,
description=new.description,
film_id=new.film_id
WHERE film_id=old.film_id;
END IF;
END$$
DELIMITER ;
Trigger "del_film"
-- Trigger for DELECT FROM film table
-- DELETE from film_text table as well
DELIMITER $$
CREATE TRIGGER `del_film` AFTER DELETE ON `film` FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
DELETE FROM film_text WHERE film_id = old.film_id;
END$$
DELIMITER ;
3. Microsoft Northwind Trader Database
For MS SQL Server, you can download the Northwind database from "Northwind and Pubs Sample Databases for SQL Server 2000". Run the downloaded ".msi" file, it will extract the files into "C:\SQL Server 2000 Sample Databases". The SQL statements are kept in "instnwnd.sql".
For MS Access ⇒ Launch Access ⇒ Choose "Sample" ⇒ Northwind Sample Database ⇒ Download.
There are various MySQL ports available. For example, "northwindextended" project @ http://code.google.com/p/northwindextended.
3.1 Database and Tables
There are 13 tables as follows:
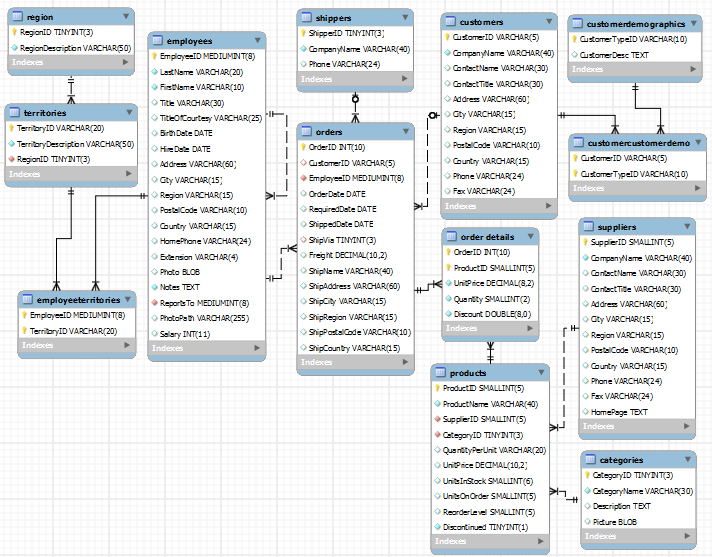
Table "Customers"
CREATE TABLE `Customers` (
`CustomerID` VARCHAR(5) NOT NULL,
-- First 5 letters of CompanyName
-- Probably better to use an UNSIGNED INT
`CompanyName` VARCHAR(40) NOT NULL,
`ContactName` VARCHAR(30),
`ContactTitle` VARCHAR(30),
`Address` VARCHAR(60),
`City` VARCHAR(15),
`Region` VARCHAR(15),
`PostalCode` VARCHAR(10),
`Country` VARCHAR(15),
`Phone` VARCHAR(24),
`Fax` VARCHAR(24),
PRIMARY KEY (`CustomerID`),
INDEX (`City`),
INDEX (`CompanyName`),
INDEX (`PostalCode`),
INDEX (`Region`)
-- Build indexes on these columns for fast search
);
There are 93 records for this table.
Table "Employees"
CREATE TABLE `Employees` (
`EmployeeID` MEDIUMINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
-- [0, 65535]
`LastName` VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
`FirstName` VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL,
`Title` VARCHAR(30), -- e.g., 'Sales Coordinator'
`TitleOfCourtesy` VARCHAR(25), -- e.g., 'Mr.' 'Ms.' (ENUM??)
`BirthDate` DATE, -- 'YYYY-MM-DD'
`HireDate` DATE,
`Address` VARCHAR(60),
`City` VARCHAR(15),
`Region` VARCHAR(15),
`PostalCode` VARCHAR(10),
`Country` VARCHAR(15),
`HomePhone` VARCHAR(24),
`Extension` VARCHAR(4),
`Photo` BLOB, -- 64KB
`Notes` TEXT NOT NULL, -- 64KB
`ReportsTo` MEDIUMINT UNSIGNED NULL, -- Manager's ID
-- Allow NULL for boss
`PhotoPath` VARCHAR(255),
`Salary` INT,
INDEX (`LastName`),
INDEX (`PostalCode`),
PRIMARY KEY (`EmployeeID`),
FOREIGN KEY (`ReportsTo`) REFERENCES `Employees` (`EmployeeID`)
);
To load this table with the sample data provided, you need to move the second record as the first record and hardcode the employeeID. There are 9 records for this table. The photos are included as hex data.
To list the worker names under the manager names, you need to join the employee table to itself. Use LEFT JOIN to retrieve ReportsTo of NULL.
-- List the worker names under the managers' ID
SELECT reportsTo AS `Manager ID`, CONCAT(employees.FirstName, ' ', employees.LastName) AS `Workers`
FROM employees
ORDER BY reportsTo;
+------------+------------------+
| Manager ID | Workers |
+------------+------------------+
| NULL | Andrew Fuller |
| 2 | Nancy Davolio |
| 2 | Janet Leverling |
| 2 | Margaret Peacock |
| 2 | Steven Buchanan |
| 2 | Laura Callahan |
| 5 | Michael Suyama |
| 5 | Robert King |
| 5 | Anne Dodsworth |
+------------+------------------+
-- List the worker name under the managers' name
-- Need to use a LEFT JOIN
SELECT
CONCAT(managers.FirstName, ' ', managers.LastName) AS `Managers`,
CONCAT(employees.FirstName, ' ', employees.LastName) AS `Workers`
FROM
employees LEFT JOIN employees AS managers ON employees.ReportsTo = managers.employeeID
ORDER BY
managers.employeeID;
+-----------------+------------------+
| Managers | Workers |
+-----------------+------------------+
| NULL | Andrew Fuller |
| Andrew Fuller | Margaret Peacock |
| Andrew Fuller | Laura Callahan |
| Andrew Fuller | Nancy Davolio |
| Andrew Fuller | Steven Buchanan |
| Andrew Fuller | Janet Leverling |
| Steven Buchanan | Robert King |
| Steven Buchanan | Anne Dodsworth |
| Steven Buchanan | Michael Suyama |
+-----------------+------------------+
Table "Region"
CREATE TABLE `Region` (
`RegionID` TINYINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
-- [0,255]
`RegionDescription` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
-- e.g., 'Eastern','Western','Northern','Southern'
-- Could use an ENUM and eliminate this table
PRIMARY KEY (`RegionID`)
);
There are 4 records for this table ('Eastern', 'Western', 'Northern', 'Southern').
Table "Territories"
-- e.g., ('02116', 'Boston', 1)
CREATE TABLE `Territories` (
`TerritoryID` VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL, -- ZIP code
`TerritoryDescription` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL, -- Name
`RegionID` TINYINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
-- Could use an ENUM to eliminate `Region` table
PRIMARY KEY (`TerritoryID`),
FOREIGN KEY (`RegionID`) REFERENCES `Region` (`RegionID`)
);
There are 53 records for this table.
Table "EmployeeTerritories"
-- Many-to-many Junction table between Employee and Territory
CREATE TABLE `EmployeeTerritories` (
`EmployeeID` MEDIUMINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
`TerritoryID` VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`EmployeeID`, `TerritoryID`),
FOREIGN KEY (`EmployeeID`) REFERENCES `Employees` (`EmployeeID`),
FOREIGN KEY (`TerritoryID`) REFERENCES `Territories` (`TerritoryID`)
);
There are 49 records for this table. Each employee has more than one territories. Some territories are not covered (53-49=4).
SELECT EmployeeID, COUNT(*) from EmployeeTerritories GROUP BY EmployeeID WITH ROLLUP;
+------------+----------+
| EmployeeID | COUNT(*) |
+------------+----------+
| 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 7 |
| 3 | 4 |
| 4 | 3 |
| 5 | 7 |
| 6 | 5 |
| 7 | 10 |
| 8 | 4 |
| 9 | 7 |
| NULL | 49 |
+------------+----------+
SELECT TerritoryID, TerritoryDescription
FROM Territories LEFT JOIN EmployeeTerritories using (TerritoryID)
WHERE EmployeeID IS NULL;
+-------------+----------------------+
| TerritoryID | TerritoryDescription |
+-------------+----------------------+
| 29202 | Columbia |
| 72716 | Bentonville |
| 75234 | Dallas |
| 78759 | Austin |
+-------------+----------------------+
Table "Categories"
CREATE TABLE `Categories` (
`CategoryID` TINYINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
-- [0, 255], not expected to be large
`CategoryName` VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL,
-- e.g., 'Beverages','Condiments',etc
`Description` TEXT, -- up to 64KB characters
`Picture` BLOB, -- up to 64KB binary
PRIMARY KEY (`CategoryID`),
UNIQUE INDEX (`CategoryName`)
-- Build index on this unique-value column for fast search
);
There are 8 records for the table, with pictures in hex code.
Table "Suppliers"
CREATE TABLE `Suppliers` (
`SupplierID` SMALLINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
-- [0, 65535]
`CompanyName` VARCHAR(40) NOT NULL,
`ContactName` VARCHAR(30),
`ContactTitle` VARCHAR(30),
`Address` VARCHAR(60),
`City` VARCHAR(15),
`Region` VARCHAR(15),
`PostalCode` VARCHAR(10),
`Country` VARCHAR(15),
`Phone` VARCHAR(24),
`Fax` VARCHAR(24),
`HomePage` TEXT, -- 64KB?? VARCHAR(255)?
PRIMARY KEY (`SupplierID`),
INDEX (`CompanyName`), -- UNIQUE?
INDEX (`PostalCode`)
);
There are 29 records for this table.
Table "Products"
CREATE TABLE `Products` (
`ProductID` SMALLINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`ProductName` VARCHAR(40) NOT NULL,
`SupplierID` SMALLINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, -- one supplier only
`CategoryID` TINYINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
`QuantityPerUnit` VARCHAR(20), -- e.g., '10 boxes x 20 bags'
`UnitPrice` DECIMAL(10,2) UNSIGNED DEFAULT 0,
`UnitsInStock` SMALLINT DEFAULT 0, -- Negative??
`UnitsOnOrder` SMALLINT UNSIGNED DEFAULT 0,
`ReorderLevel` SMALLINT UNSIGNED DEFAULT 0,
`Discontinued` BOOLEAN NOT NULL DEFAULT FALSE,
PRIMARY KEY (`ProductID`),
INDEX (`ProductName`),
FOREIGN KEY (`CategoryID`) REFERENCES `Categories` (`CategoryID`),
FOREIGN KEY (`SupplierID`) REFERENCES `Suppliers` (`SupplierID`)
);
There are 77 records for this table.
Table "Shippers"
CREATE TABLE `Shippers` (
`ShipperID` TINYINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`CompanyName` VARCHAR(40) NOT NULL,
`Phone` VARCHAR(24),
PRIMARY KEY (`ShipperID`)
);
There are 3 records for this table.
Table "Orders"
CREATE TABLE `Orders` (
`OrderID` INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
-- Use UNSIGNED INT to avoid run-over
`CustomerID` VARCHAR(5),
`EmployeeID` MEDIUMINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
`OrderDate` DATE,
`RequiredDate` DATE,
`ShippedDate` DATE,
`ShipVia` TINYINT UNSIGNED,
`Freight` DECIMAL(10,2) UNSIGNED DEFAULT 0,
`ShipName` VARCHAR(40),
`ShipAddress` VARCHAR(60),
`ShipCity` VARCHAR(15),
`ShipRegion` VARCHAR(15),
`ShipPostalCode` VARCHAR(10),
`ShipCountry` VARCHAR(15),
PRIMARY KEY (`OrderID`),
INDEX (`OrderDate`),
INDEX (`ShippedDate`),
INDEX (`ShipPostalCode`),
FOREIGN KEY (`CustomerID`) REFERENCES `Customers` (`CustomerID`),
FOREIGN KEY (`EmployeeID`) REFERENCES `Employees` (`EmployeeID`),
FOREIGN KEY (`ShipVia`) REFERENCES `Shippers` (`ShipperID`)
);
There are 830 records for this table.
Table "Order Details"
-- Many-to-many Junction table between Orders and Products
CREATE TABLE `Order Details` (
`OrderID` INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
`ProductID` SMALLINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
`UnitPrice` DECIMAL(8,2) UNSIGNED NOT NULL DEFAULT 999999.99,
-- max value as default
`Quantity` SMALLINT(2) UNSIGNED NOT NULL DEFAULT 1,
`Discount` DOUBLE(8,0) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0, -- e.g., 0.15
PRIMARY KEY (`OrderID`, `ProductID`),
FOREIGN KEY (`OrderID`) REFERENCES `Orders` (`OrderID`),
FOREIGN KEY (`ProductID`) REFERENCES `Products` (`ProductID`)
);
There are 2155 records for this table.
-- List the number of `Order Details` for each OrderID
SELECT OrderID, COUNT(OrderID)
FROM Orders INNER JOIN `Order Details` USING (OrderID)
GROUP BY OrderID
WITH ROLLUP;
Table "CustomerDemographics"
CREATE TABLE `CustomerDemographics` (
`CustomerTypeID` VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL,
`CustomerDesc` TEXT, -- 64KB
PRIMARY KEY (`CustomerTypeID`)
);
No record is provided for this table?!
Table "CustomerCustomerDemo"
CREATE TABLE `CustomerCustomerDemo` (
`CustomerID` VARCHAR(5) NOT NULL,
`CustomerTypeID` VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`CustomerID`, `CustomerTypeID`),
FOREIGN KEY (`CustomerTypeID`) REFERENCES `CustomerDemographics` (`CustomerTypeID`),
FOREIGN KEY (`CustomerID`) REFERENCES `Customers` (`CustomerID`)
);
No record is provided for this table too?!
3.2 Views
There are 16 views defined.
View "Current Product List"
-- List current products (not discontinued)
CREATE VIEW `Current Product List`
AS
SELECT
ProductID,
ProductName
FROM Products
WHERE Discontinued = 0;
View "Alphabetical list of products"
-- List products (with category) order by ProductID
-- which is arranged alphabetically in ProductName
CREATE VIEW `Alphabetical list of products`
AS
SELECT
Products.*,
Categories.CategoryName
FROM Categories
INNER JOIN Products ON Categories.CategoryID = Products.CategoryID
WHERE Products.Discontinued = 0; -- FALSE
-- Example
mysql> SELECT * FROM `Alphabetical list of products` LIMIT 1 \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
ProductID: 1
ProductName: Chai
SupplierID: 1
CategoryID: 1
QuantityPerUnit: 10 boxes x 20 bags
UnitPrice: 18.00
UnitsInStock: 39
UnitsOnOrder: 0
ReorderLevel: 10
Discontinued: 0
CategoryName: Beverages
View "Products by Category"
-- List all products grouped by category
CREATE VIEW `Products by Category`
AS
SELECT
Categories.CategoryName,
Products.ProductName,
Products.QuantityPerUnit,
Products.UnitsInStock,
Products.Discontinued
FROM Categories
INNER JOIN Products ON Categories.CategoryID = Products.CategoryID
WHERE Products.Discontinued = 0; -- FALSE
-- Example
mysql> SELECT * FROM `Products by Category`;
+----------------+----------------------------------+----------------------+--------------+--------------+
| CategoryName | ProductName | QuantityPerUnit | UnitsInStock | Discontinued |
+----------------+----------------------------------+----------------------+--------------+--------------+
| Beverages | Chai | 10 boxes x 20 bags | 39 | 0 |
| Beverages | Chang | 24 - 12 oz bottles | 17 | 0 |
| Beverages | Sasquatch Ale | 24 - 12 oz bottles | 111 | 0 |
.......
View "Products Above Average Price"
CREATE VIEW `Products Above Average Price`
AS
SELECT
Products.ProductName,
Products.UnitPrice
FROM Products
WHERE Products.UnitPrice > (SELECT AVG(UnitPrice) From Products); -- subquery
mysql> SELECT * FROM `Products Above Average Price` ORDER BY UnitPrice DESC;
+---------------------------------+-----------+
| ProductName | UnitPrice |
+---------------------------------+-----------+
| Cte de Blaye | 263.50 |
| Thringer Rostbratwurst | 123.79 |
| Mishi Kobe Niku | 97.00 |
......
View "Customer and Suppliers by City"
-- List all customers and suppliers (with an union)
-- order by City and CompanyName
CREATE VIEW `Customer and Suppliers by City`
AS
SELECT
City,
CompanyName,
ContactName,
'Customers' AS Relationship
FROM Customers
UNION -- Union two result sets (of same column numbers), remove duplicates
SELECT City,
CompanyName,
ContactName,
'Suppliers'
FROM Suppliers
ORDER BY City, CompanyName;
mysql> SELECT * FROM `Customer and Suppliers by City` LIMIT 10;
+--------------+----------------------------+------------------+--------------+
| City | CompanyName | ContactName | Relationship |
+--------------+----------------------------+------------------+--------------+
| NULL | IT | Val2 | Customers |
| NULL | IT | Valon Hoti | Customers |
| Aachen | Drachenblut Delikatessen | Sven Ottlieb | Customers |
| Albuquerque | Rattlesnake Canyon Grocery | Paula Wilson | Customers |
| Anchorage | Old World Delicatessen | Rene Phillips | Customers |
| Ann Arbor | Grandma Kelly's Homestead | Regina Murphy | Suppliers |
......
View "Order Details Extended"
-- Extend `Order Details` to include ProductName and TotalPrice
CREATE VIEW `Order Details Extended`
AS
SELECT
`Order Details`.OrderID,
`Order Details`.ProductID,
Products.ProductName,
`Order Details`.UnitPrice,
`Order Details`.Quantity,
`Order Details`.Discount,
ROUND(`Order Details`.UnitPrice*Quantity*(1-Discount)) AS ExtendedPrice
FROM Products
JOIN `Order Details` ON Products.ProductID = `Order Details`.ProductID;
mysql> SELECT * FROM `Order Details Extended`;
+---------+-----------+--------------+-----------+----------+----------+---------------+
| OrderID | ProductID | ProductName | UnitPrice | Quantity | Discount | ExtendedPrice |
+---------+-----------+--------------+-----------+----------+----------+---------------+
| 10265 | 17 | Alice Mutton | 31.20 | 30 | 0 | 936 |
| 10279 | 17 | Alice Mutton | 31.20 | 15 | 0 | 468 |
| 10294 | 17 | Alice Mutton | 31.20 | 15 | 0 | 468 |
......
View "Invoices"
-- All information (order, customer, shipper)
-- for each `Order Details` line.
-- An invoice is supposed to be per order?!
CREATE VIEW `Invoices`
AS
SELECT
Orders.ShipName,
Orders.ShipAddress,
Orders.ShipCity,
Orders.ShipRegion,
Orders.ShipPostalCode,
Orders.ShipCountry,
Orders.CustomerID,
Customers.CompanyName AS CustomerName,
Customers.Address,
Customers.City,
Customers.Region,
Customers.PostalCode,
Customers.Country,
(Employees.FirstName + ' ' + Employees.LastName) AS Salesperson,
Orders.OrderID,
Orders.OrderDate,
Orders.RequiredDate,
Orders.ShippedDate,
Shippers.CompanyName As ShipperName,
`Order Details`.ProductID,
Products.ProductName,
`Order Details`.UnitPrice,
`Order Details`.Quantity,
`Order Details`.Discount,
FLOOR(`Order Details`.UnitPrice*Quantity*(1-Discount)) AS ExtendedPrice,
-- truncate to nearest dollars
Orders.Freight
FROM Customers
JOIN Orders ON Customers.CustomerID = Orders.CustomerID
JOIN Employees ON Employees.EmployeeID = Orders.EmployeeID
JOIN `Order Details` ON Orders.OrderID = `Order Details`.OrderID
JOIN Products ON Products.ProductID = `Order Details`.ProductID
JOIN Shippers ON Shippers.ShipperID = Orders.ShipVia;
-- Example
mysql> SELECT * FROM `Invoices` LIMIT 2 \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
ShipName: Ernst Handel
......
CustomerID: ERNSH
CustomerName: Ernst Handel
......
Salesperson: 0
OrderID: 10258
OrderDate: 1996-07-17
RequiredDate: 1996-08-14
ShippedDate: 1996-07-23
ShipperName: Speedy Express
ProductID: 2
ProductName: Chang
UnitPrice: 15.20
Quantity: 50
Discount: 0
ExtendedPrice: 760
Freight: 140.51
*************************** 2. row ***************************
ShipName: Ernst Handel
......
CustomerID: ERNSH
CustomerName: Ernst Handel
......
Salesperson: 0
OrderID: 10258
OrderDate: 1996-07-17
RequiredDate: 1996-08-14
ShippedDate: 1996-07-23
ShipperName: Speedy Express
ProductID: 5
ProductName: Chef Anton's Gumbo Mix
UnitPrice: 17.00
Quantity: 65
Discount: 0
ExtendedPrice: 1105
Freight: 140.51
View "Orders Qry"
-- List details (order and customer) of each order
-- for customer query
CREATE VIEW `Orders Qry`
AS
SELECT
Orders.OrderID,
Orders.CustomerID,
Orders.EmployeeID,
Orders.OrderDate,
Orders.RequiredDate,
Orders.ShippedDate,
Orders.ShipVia,
Orders.Freight,
Orders.ShipName,
Orders.ShipAddress,
Orders.ShipCity,
Orders.ShipRegion,
Orders.ShipPostalCode,
Orders.ShipCountry,
Customers.CompanyName,
Customers.Address,
Customers.City,
Customers.Region,
Customers.PostalCode,
Customers.Country
FROM Customers
JOIN Orders ON Customers.CustomerID = Orders.CustomerID;
-- Example
mysql> SELECT * FROM `Orders Qry` LIMIT 1 \G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
OrderID: 10643
CustomerID: ALFKI
EmployeeID: 6
OrderDate: 1997-08-25
RequiredDate: 1997-09-22
ShippedDate: 1997-09-02
ShipVia: 1
Freight: 29.46
ShipName: Alfreds Futterkiste
......
CompanyName: Alfreds Futterkiste
......
View "Product Sales for 1997"
-- List sales for each productName for 1997
CREATE VIEW `Product Sales for 1997`
AS
SELECT
Categories.CategoryName,
Products.ProductName,
Sum(ROUND(`Order Details`.UnitPrice*Quantity*(1-Discount))) AS ProductSales
FROM Categories
JOIN Products On Categories.CategoryID = Products.CategoryID
JOIN `Order Details` on Products.ProductID = `Order Details`.ProductID
JOIN `Orders` on Orders.OrderID = `Order Details`.OrderID
WHERE Orders.ShippedDate BETWEEN '1997-01-01' And '1997-12-31'
GROUP BY Categories.CategoryName, Products.ProductName;
-- Example
mysql> SELECT * FROM `Product Sales for 1997`;
+----------------+----------------------------------+--------------+
| CategoryName | ProductName | ProductSales |
+----------------+----------------------------------+--------------+
| Beverages | Chai | 5296 |
| Beverages | Chang | 7600 |
| Beverages | Chartreuse verte | 4928 |
......
View "Sales by Category"
-- List Sales by ProductName
CREATE VIEW `Sales by Category`
AS
SELECT
Categories.CategoryID,
Categories.CategoryName,
Products.ProductName,
Sum(`Order Details Extended`.ExtendedPrice) AS ProductSales
FROM Categories
JOIN Products ON Categories.CategoryID = Products.CategoryID
JOIN `Order Details Extended` ON Products.ProductID = `Order Details Extended`.ProductID
JOIN Orders ON Orders.OrderID = `Order Details Extended`.OrderID
WHERE Orders.OrderDate BETWEEN '1997-01-01' And '1997-12-31'
GROUP BY
Categories.CategoryID,
Categories.CategoryName,
Products.ProductName;
mysql> SELECT * FROM `Sales by Category`;
+------------+----------------+----------------------------------+--------------+
| CategoryID | CategoryName | ProductName | ProductSales |
+------------+----------------+----------------------------------+--------------+
| 1 | Beverages | Chai | 5296 |
| 1 | Beverages | Chang | 7600 |
| 1 | Beverages | Chartreuse verte | 4928 |
......
View "Category Sales for 1997"
CREATE VIEW `Category Sales for 1997`
AS
SELECT
`Product Sales for 1997`.CategoryName, -- Use `Product Sales for 1997` view
Sum(`Product Sales for 1997`.ProductSales) AS CategorySales
FROM `Product Sales for 1997`
GROUP BY `Product Sales for 1997`.CategoryName;
mysql> SELECT * FROM `Category Sales for 1997`;
+----------------+---------------+
| CategoryName | CategorySales |
+----------------+---------------+
| Beverages | 108547 |
| Condiments | 59586 |
| Confections | 85678 |
......
View "Quarterly Orders"
-- List sales by customers in 1997
CREATE VIEW `Quarterly Orders`
AS
SELECT DISTINCT
Customers.CustomerID,
Customers.CompanyName,
Customers.City,
Customers.Country
FROM Customers
JOIN Orders ON Customers.CustomerID = Orders.CustomerID
WHERE Orders.OrderDate BETWEEN '1997-01-01' And '1997-12-31';
mysql> SELECT * FROM `Quarterly Orders`;
+------------+------------------------------------+-----------------+-------------+
| CustomerID | CompanyName | City | Country |
+------------+------------------------------------+-----------------+-------------+
| ALFKI | Alfreds Futterkiste | Berlin | Germany |
| ANATR | Ana Trujillo Emparedados y helados | Mxico D.F. | Mexico |
| ANTON | Antonio Moreno Taquera | Mxico D.F. | Mexico |
.......
View "Order Subtotals"
-- List the total amount for each order
CREATE VIEW `Order Subtotals`
AS
SELECT
`Order Details`.OrderID,
Sum(ROUND(`Order Details`.UnitPrice*Quantity*(1-Discount))) AS Subtotal
FROM `Order Details`
GROUP BY `Order Details`.OrderID;
-- Example
mysql> SELECT * FROM `Order Subtotals` LIMIT 5;
+---------+----------+
| OrderID | Subtotal |
+---------+----------+
| 10248 | 440 |
| 10249 | 1863 |
| 10250 | 1813 |
| 10251 | 671 |
| 10252 | 3730 |
+---------+----------+
View "Sales Totals by Amount"
CREATE VIEW `Sales Totals by Amount`
AS
SELECT
`Order Subtotals`.Subtotal AS SaleAmount, -- `Order Subtotals` is a view
Orders.OrderID,
Customers.CompanyName,
Orders.ShippedDate
FROM Customers
JOIN Orders ON Customers.CustomerID = Orders.CustomerID
JOIN `Order Subtotals` ON Orders.OrderID = `Order Subtotals`.OrderID
WHERE (`Order Subtotals`.Subtotal > 2500)
AND (Orders.ShippedDate BETWEEN '1997-01-01' And '1997-12-31');
-- Example
mysql> SELECT * FROM `Sales Totals by Amount`;
+------------+---------+------------------------------+-------------+
| SaleAmount | OrderID | CompanyName | ShippedDate |
+------------+---------+------------------------------+-------------+
| 3302 | 10393 | Save-a-lot Markets | 1997-01-03 |
| 2736 | 10398 | Save-a-lot Markets | 1997-01-09 |
| 3063 | 10400 | Eastern Connection | 1997-01-16 |
......
View "Summary of Sales by Quarter"
CREATE VIEW `Summary of Sales by Quarter`
AS
SELECT
Orders.ShippedDate,
Orders.OrderID,
`Order Subtotals`.Subtotal -- Use `Order Subtotals` view
FROM Orders
INNER JOIN `Order Subtotals` ON Orders.OrderID = `Order Subtotals`.OrderID
WHERE Orders.ShippedDate IS NOT NULL;
-- Example
mysql> SELECT * FROM `Summary of Sales by Quarter`;
+-------------+---------+----------+
| ShippedDate | OrderID | Subtotal |
+-------------+---------+----------+
| 1996-07-16 | 10248 | 440 |
| 1996-07-10 | 10249 | 1863 |
| 1996-07-12 | 10250 | 1813 |
......
View "Summary of Sales by Year"
-- List each order
CREATE VIEW `Summary of Sales by Year`
AS
SELECT
Orders.ShippedDate,
Orders.OrderID,
`Order Subtotals`.Subtotal
FROM Orders
INNER JOIN `Order Subtotals` ON Orders.OrderID = `Order Subtotals`.OrderID
WHERE Orders.ShippedDate IS NOT NULL;
-- Example
mysql> SELECT * FROM `Summary of Sales by Year`;
+-------------+---------+----------+
| ShippedDate | OrderID | Subtotal |
+-------------+---------+----------+
| 1996-07-16 | 10248 | 440 |
| 1996-07-10 | 10249 | 1863 |
| 1996-07-12 | 10250 | 1813 |
......
3.3 Stored Routines: Procedures and Functions
There are 7 procedures defined.
Procedure "CustOrdersDetail"
-- Given an OrderID, print `Order Details`
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE `CustOrdersDetail`(IN AtOrderID INT)
BEGIN
SELECT ProductName,
`Order Details`.UnitPrice,
Quantity,
Discount * 100 AS `Discount`,
ROUND(Quantity * (1 - Discount) * `Order Details`.UnitPrice) AS ExtendedPrice
FROM Products INNER JOIN `Order Details` USING (ProductID)
WHERE `Order Details`.OrderID = AtOrderID;
END$$
DELIMITER ;
mysql> CALL `CustOrdersDetail`(10250);
+----------------------------------+-----------+----------+----------+---------------+
| ProductName | UnitPrice | Quantity | Discount | ExtendedPrice |
+----------------------------------+-----------+----------+----------+---------------+
| Jack's New England Clam Chowder | 7.70 | 10 | 0 | 77 |
| Manjimup Dried Apples | 42.40 | 35 | 0 | 1484 |
| Louisiana Fiery Hot Pepper Sauce | 16.80 | 15 | 0 | 252 |
+----------------------------------+-----------+----------+----------+---------------+
Procedure "CustOrdersOrders"
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE `CustOrdersOrders`(IN AtCustomerID VARCHAR(5))
BEGIN
SELECT
OrderID,
OrderDate,
RequiredDate,
ShippedDate
FROM Orders
WHERE CustomerID = AtCustomerID
ORDER BY OrderID;
END $$
DELIMITER ;
mysql> CALL `CustOrdersOrders`('ANTON');
+---------+------------+--------------+-------------+
| OrderID | OrderDate | RequiredDate | ShippedDate |
+---------+------------+--------------+-------------+
| 10365 | 1996-11-27 | 1996-12-25 | 1996-12-02 |
| 10507 | 1997-04-15 | 1997-05-13 | 1997-04-22 |
| 10535 | 1997-05-13 | 1997-06-10 | 1997-05-21 |
......
Procedure "CustOrderHist"
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE `CustOrderHist`(IN AtCustomerID VARCHAR(5))
BEGIN
SELECT
ProductName,
SUM(Quantity) as TOTAL
FROM Products
INNER JOIN `Order Details` USING(ProductID)
INNER JOIN Orders USING (OrderID)
INNER JOIN Customers USING (CustomerID)
WHERE Customers.CustomerID = AtCustomerID
GROUP BY ProductName;
END $$
DELIMITER ;
mysql> CALL `CustOrderHist`('ANTON');
+-------------------------------+-------+
| ProductName | TOTAL |
+-------------------------------+-------+
| Alice Mutton | 18 |
| Boston Crab Meat | 10 |
| Chang | 20 |
......
Procedure "Ten Most Expensive Products"
DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS `Ten Most Expensive Products`;
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE `Ten Most Expensive Products`()
BEGIN
SELECT
Products.ProductName AS TenMostExpensiveProducts,
Products.UnitPrice
FROM Products
ORDER BY Products.UnitPrice DESC
LIMIT 10;
END $$
DELIMITER ;
mysql> CALL `Ten Most Expensive Products`;
+--------------------------+-----------+
| TenMostExpensiveProducts | UnitPrice |
+--------------------------+-----------+
| Cte de Blaye | 263.50 |
| Thringer Rostbratwurst | 123.79 |
| Mishi Kobe Niku | 97.00 |
......
Procedure "Employee Sales by Country"
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE `Employee Sales by Country`(IN AtBeginning_Date DATE, IN AtEnding_Date DATE)
BEGIN
SELECT
Employees.Country,
Employees.LastName,
Employees.FirstName,
Orders.ShippedDate,
Orders.OrderID,
`Order Subtotals`.Subtotal AS SaleAmount
FROM Employees
INNER JOIN Orders ON Employees.EmployeeID = Orders.EmployeeID
INNER JOIN `Order Subtotals` ON Orders.OrderID = `Order Subtotals`.OrderID
WHERE Orders.ShippedDate BETWEEN AtBeginning_Date AND AtEnding_Date;
END $$
DELIMITER ;
mysql> CALL `Employee Sales by Country`('1997-01-01', '1997-01-31');
+---------+-----------+-----------+-------------+---------+------------+
| Country | LastName | FirstName | ShippedDate | OrderID | SaleAmount |
+---------+-----------+-----------+-------------+---------+------------+
| USA | Callahan | Laura | 1997-01-16 | 10380 | 1420 |
| USA | Fuller | Andrew | 1997-01-01 | 10392 | 1440 |
| USA | Davolio | Nancy | 1997-01-03 | 10393 | 3302 |
......
Procedure "Sales by Year"
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE `Sales by Year`(IN AtBeginning_Date DATE, IN AtEnding_Date DATE)
BEGIN
SELECT
Orders.ShippedDate,
Orders.OrderID,
`Order Subtotals`.Subtotal,
ShippedDate AS Year
FROM Orders
JOIN `Order Subtotals` ON Orders.OrderID = `Order Subtotals`.OrderID
WHERE Orders.ShippedDate BETWEEN AtBeginning_Date AND AtEnding_Date;
END $$
DELIMITER ;
mysql> CALL `Sales by Year`('1997-01-01', '1997-01-31');
+-------------+---------+----------+------------+
| ShippedDate | OrderID | Subtotal | Year |
+-------------+---------+----------+------------+
| 1997-01-16 | 10380 | 1420 | 1997-01-16 |
| 1997-01-01 | 10392 | 1440 | 1997-01-01 |
| 1997-01-03 | 10393 | 3302 | 1997-01-03 |
......
Procedure "SalesByCategory"
DELIMITER $$
CREATE PROCEDURE `SalesByCategory`(IN AtCategoryName VARCHAR(15), IN AtOrdYear VARCHAR(4))
BEGIN
SELECT
ProductName,
ROUND(SUM(OD.Quantity * (1-OD.Discount) * OD.UnitPrice)) AS TotalPurchase
FROM `Order Details` AS OD
INNER JOIN Orders AS O USING (OrderID)
INNER JOIN Products AS P USING (ProductID)
INNER JOIN Categories AS C USING (CategoryID)
WHERE C.CategoryName = AtCategoryName
AND YEAR(O.OrderDate) = AtOrdYear
GROUP BY ProductName
ORDER BY ProductName;
END $$
DELIMITER ;
mysql> CALL `SalesByCategory`('Beverages', 1997);
+---------------------------+---------------+
| ProductName | TotalPurchase |
+---------------------------+---------------+
| Chai | 5296 |
| Chang | 7600 |
| Chartreuse verte | 4928 |
......
Try: i18n and UTF8 on MySQL Workbench.
4. MySQLTutorial.org's Sample Retailer Database
Reference: The "Classic Models" Retailer database of http://www.mysqltutorial.org.
4.1 Database and Tables
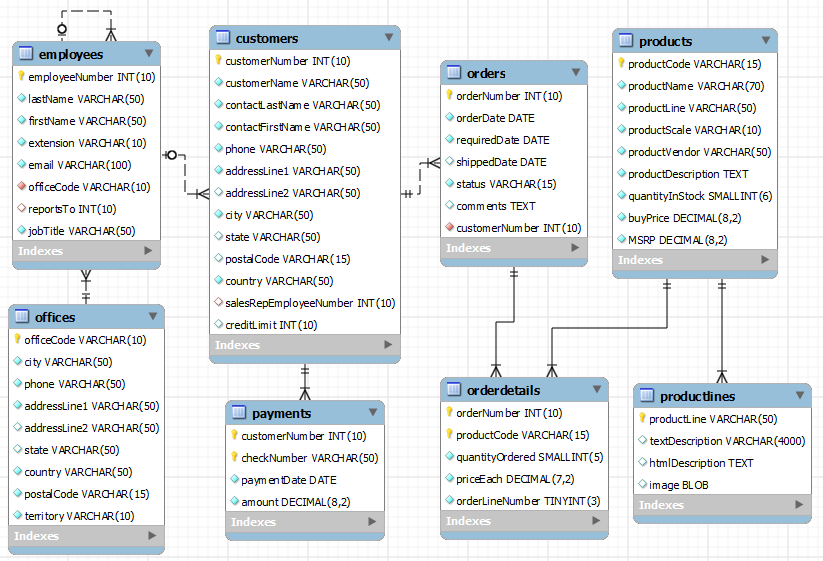
There are 8 tables, with no stored objects (view, procedure, function, trigger and event) defined.
I made some modifications to the data type, and added in the foreign keys and indexes.
Table "offices"
CREATE TABLE `offices` (
`officeCode` VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL,
`city` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
`phone` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
`addressLine1` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
`addressLine2` VARCHAR(50) DEFAULT NULL,
`state` VARCHAR(50) DEFAULT NULL,
`country` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
`postalCode` VARCHAR(15) NOT NULL,
`territory` VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`officeCode`),
INDEX (`phone`),
INDEX (`city`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
There are 7 records for this table.
Table "employees"
CREATE TABLE `employees` (
`employeeNumber` INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`lastName` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
`firstName` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
`extension` VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL,
`email` VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
`officeCode` VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL,
`reportsTo` INT UNSIGNED DEFAULT NULL,
`jobTitle` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`employeeNumber`),
INDEX (`lastName`),
INDEX (`firstName`),
FOREIGN KEY (`reportsTo`) REFERENCES `employees` (`employeeNumber`)
ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE CASCADE,
FOREIGN KEY (`officeCode`) REFERENCES `offices` (`officeCode`)
ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE CASCADE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
There are 23 records for this table.
Table "customers"
CREATE TABLE `customers` (
`customerNumber` INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`customerName` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
`contactLastName` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
`contactFirstName` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
`phone` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
`addressLine1` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
`addressLine2` VARCHAR(50) DEFAULT NULL,
`city` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
`state` VARCHAR(50) DEFAULT NULL,
`postalCode` VARCHAR(15) DEFAULT NULL,
`country` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
`salesRepEmployeeNumber` INT UNSIGNED DEFAULT NULL,
`creditLimit` INT UNSIGNED DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`customerNumber`),
INDEX (`customerName`),
INDEX (`contactLastName`),
INDEX (`contactFirstName`),
INDEX (`phone`),
INDEX (`postalCode`),
FOREIGN KEY (`salesRepEmployeeNumber`) REFERENCES `employees` (`employeeNumber`)
ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE CASCADE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
There are 122 records for this table.
Table "products"
CREATE TABLE `products` (
`productCode` VARCHAR(15) NOT NULL,
`productName` VARCHAR(70) NOT NULL,
`productLine` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
`productScale` VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL,
`productVendor` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
`productDescription` TEXT NOT NULL, -- 64KB
`quantityInStock` SMALLINT NOT NULL, -- Allow negative
`buyPrice` DECIMAL(8,2) UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
`MSRP` DECIMAL(8,2) UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`productCode`),
INDEX (`productName`),
INDEX (`productVendor`),
INDEX (`productLine`) -- needed to be indexed to be used as foreign key
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
There are 110 records for this table.
Table "productlines"
CREATE TABLE `productlines` (
`productLine` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
`textDescription` VARCHAR(4000) DEFAULT NULL,
`htmlDescription` TEXT DEFAULT NULL, -- 64 KB
`image` BLOB DEFAULT NULL, -- 64 KB
PRIMARY KEY (`productLine`),
FOREIGN KEY (`productLine`) REFERENCES `products` (`productLine`)
ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE CASCADE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
You need to index the productLine column of the products table to use the column as a foreign key here.
There are 7 records for this table.
Table "orders"
CREATE TABLE `orders` (
`orderNumber` INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`orderDate` DATE NOT NULL,
`requiredDate` DATE NOT NULL,
`shippedDate` DATE DEFAULT NULL,
`status` VARCHAR(15) NOT NULL, -- use ENUM
`comments` TEXT DEFAULT NULL,
`customerNumber` INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`orderNumber`),
INDEX (`orderDate`),
INDEX (`customerNumber`),
FOREIGN KEY (`customerNumber`) REFERENCES `customers` (`customerNumber`)
ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE CASCADE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
There are 326 records for this table.
Table "orderdetails"
CREATE TABLE `orderdetails` (
`orderNumber` INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
`productCode` VARCHAR(15) NOT NULL,
`quantityOrdered` SMALLINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, -- [0, 65535]
`priceEach` DECIMAL(7,2) NOT NULL,
`orderLineNumber` TINYINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, -- [0,255]
PRIMARY KEY (`orderNumber`,`productCode`),
FOREIGN KEY (`orderNumber`) REFERENCES `orders` (`orderNumber`)
ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE CASCADE,
FOREIGN KEY (`productCode`) REFERENCES `products` (`productCode`)
ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE CASCADE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
There are 2996 records for this table.
Table "payments"
CREATE TABLE `payments` (
`customerNumber` INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
`checkNumber` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
`paymentDate` DATE NOT NULL,
`amount` DECIMAL(8,2) UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`customerNumber`,`checkNumber`),
FOREIGN KEY (`customerNumber`) REFERENCES `customers` (`customerNumber`)
ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE CASCADE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
This payment table does not reflect the order paid?! Could also provide a VIEW for invoices.
There are 273 records for this table.
























